Population : 2 366 515 habitants (est. 2002)
Pays voisins : Estonie, Russie, Biélorussie, Lituanie
Densité : 36.64 hab./km²
Superficie : 64 589 km²
Capitale : Riga
Principales villes : Daugavpils, Liepaja, Jelgava, Jurmala, Ventspils, Rezekne
Point culminant : Gaizinkalns 312 m.
Langue(s) parlée(s) : Letton, Russe
Langue(s) officielle(s) : Letton
Monnaie :
Fête nationale : 18 novembre
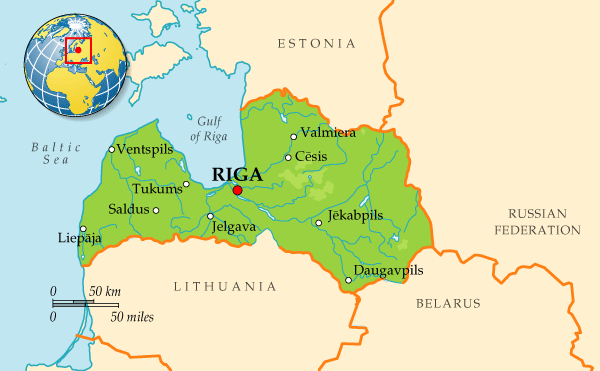
Pays voisins : Estonie, Russie, Biélorussie, Lituanie
Densité : 36.64 hab./km²
Superficie : 64 589 km²
Capitale : Riga
Principales villes : Daugavpils, Liepaja, Jelgava, Jurmala, Ventspils, Rezekne
Point culminant : Gaizinkalns 312 m.
Langue(s) parlée(s) : Letton, Russe
Langue(s) officielle(s) : Letton
Monnaie :
Fête nationale : 18 novembre

Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia (border length 343 km), to the south by Lithuania (588 km), to the east by the Russian Federation (276 km), to the southeast by Belarus (141 km), and a territory of it is one of the least populous and least densely populated countries of the European Union. The capital of Latvia is Riga. The official language is Latvian and the currency is called Lats (Ls). The country has a temperate seasonal climate.
The Latvians are a Baltic people, culturally related to the Lithuanians. Together with the Finnic Livs (or Livonians), the Latvians are the indigenous people of Latvia. and 25.5% in Estonia) of whom some are non-citizens. Latvia is historically predominantly Protestant, except for the region of Latgalia in the southeast which has historically been predominantly Roman Catholic.
Latvia is a unitary parliamentary republic and is divided into 118 administrative divisions of which 109 are municipalities and 9 are cities. There are five planning regions: Courland (Kurzeme), Latgalia (Latgale), Riga (Rīga), Vidzeme and Zemgale. The Republic of Latvia was founded on November 18, 1918. It was occupied and annexed by the Soviet Union between 1940–1941 and 1945–1991 and by Nazi Germany between 1941–1945. The peaceful "Singing Revolution" between 1987 and 1991 and "Baltic Way" demonstration on August 23, 1989 led to the independence of the Baltic states. Latvia declared the restoration of its de facto independence on August 21, 1991.
Latvia is a member of the United Nations, European Union, Council of Europe, NATO, Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, International Monetary Fund and World Trade Organization, and is part of the Schengen Area. It was a member of the League of Nations (1921–1946) and the Baltic Free Trade Area (1994–2004). Latvia is also a member of the Council of the Baltic Sea States and Nordic Investment Bank, and is together with Estonia and Lithuania involved in trilateral Baltic States cooperation and Nordic-Baltic cooperation.
After economic stagnation in the early 1990s, Latvia posted Europe-leading GDP growth figures during 1998–2006. In the global financial crisis of 2008–2010 Latvia was the hardest hit of the European Union member states, with a GDP decline of 26.54% in that period. Commentators noted signs of stabilisation in the Latvian economy by 2010, and the state of the economy continued to improve, as Latvia once again became one of the fastest growing economies of the EU in 2011. The United Nations lists Latvia as a country with a "Very High" Human Development Index (HDI).





